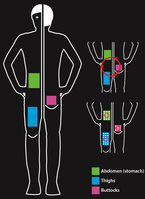
How to select the correct injection site
The most commonly used body site for injection is the abdomen, followed by the thighs and buttocks. At the various parts of the body, the thickness of subcutaneous fatty tissue is very different: the thicker the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the slower insulin is absorbed from this area into the body. The acting of insulin can be controlled this way!
Health care professionals often recommend during the diabetes training to use different injection sites at different times of the day.